An Algorithm (also called a column algorithm) is a Data Block whose values are calculated by a formula that is typically based on other Data Blocks.
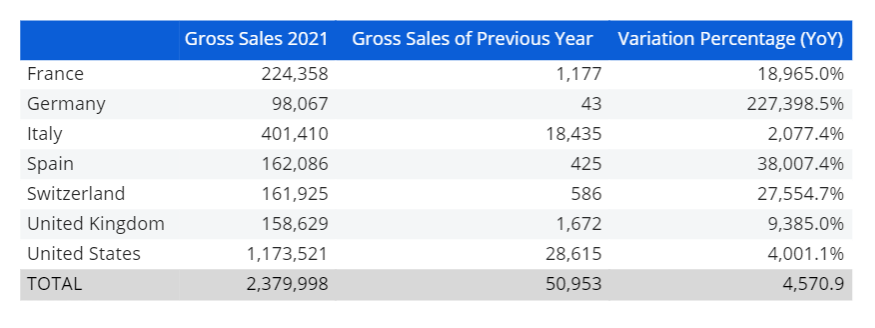
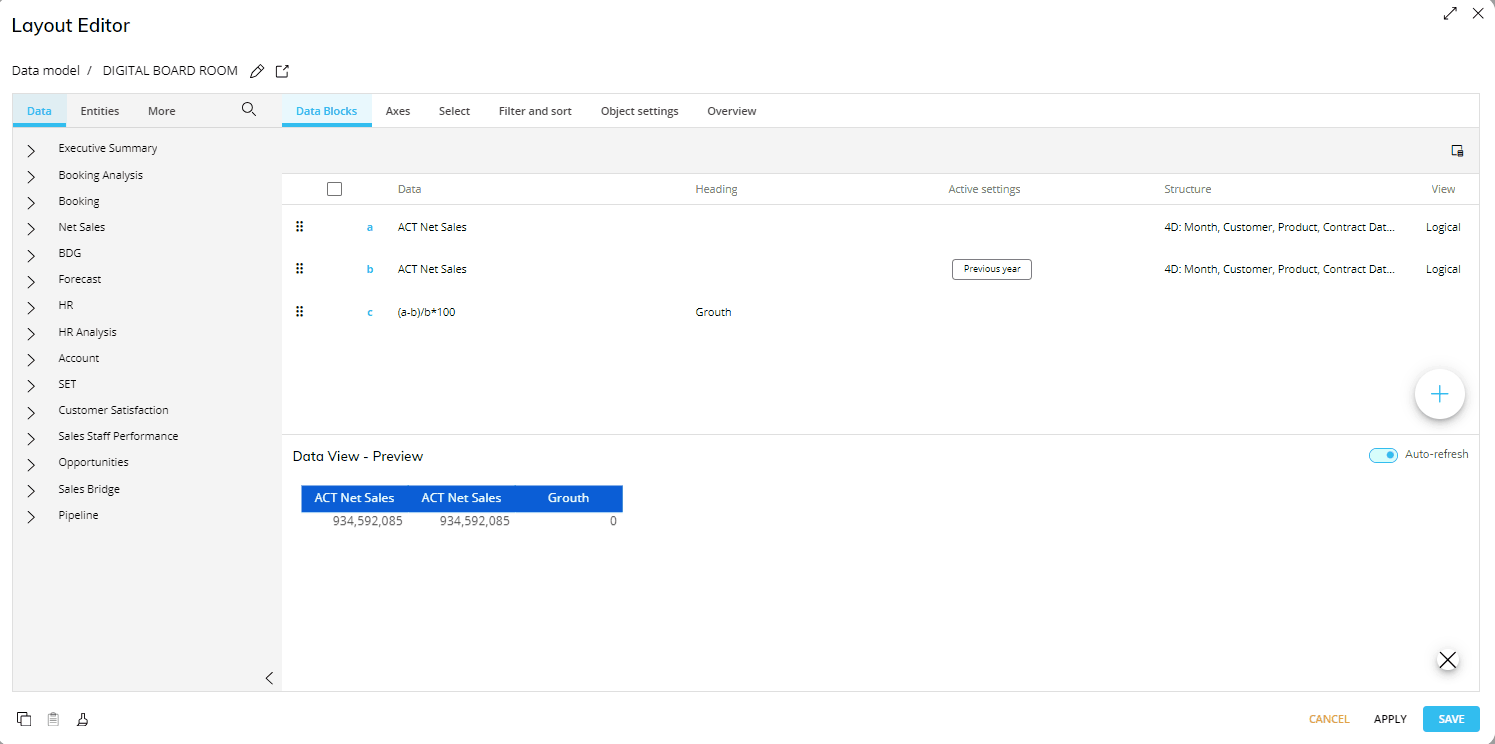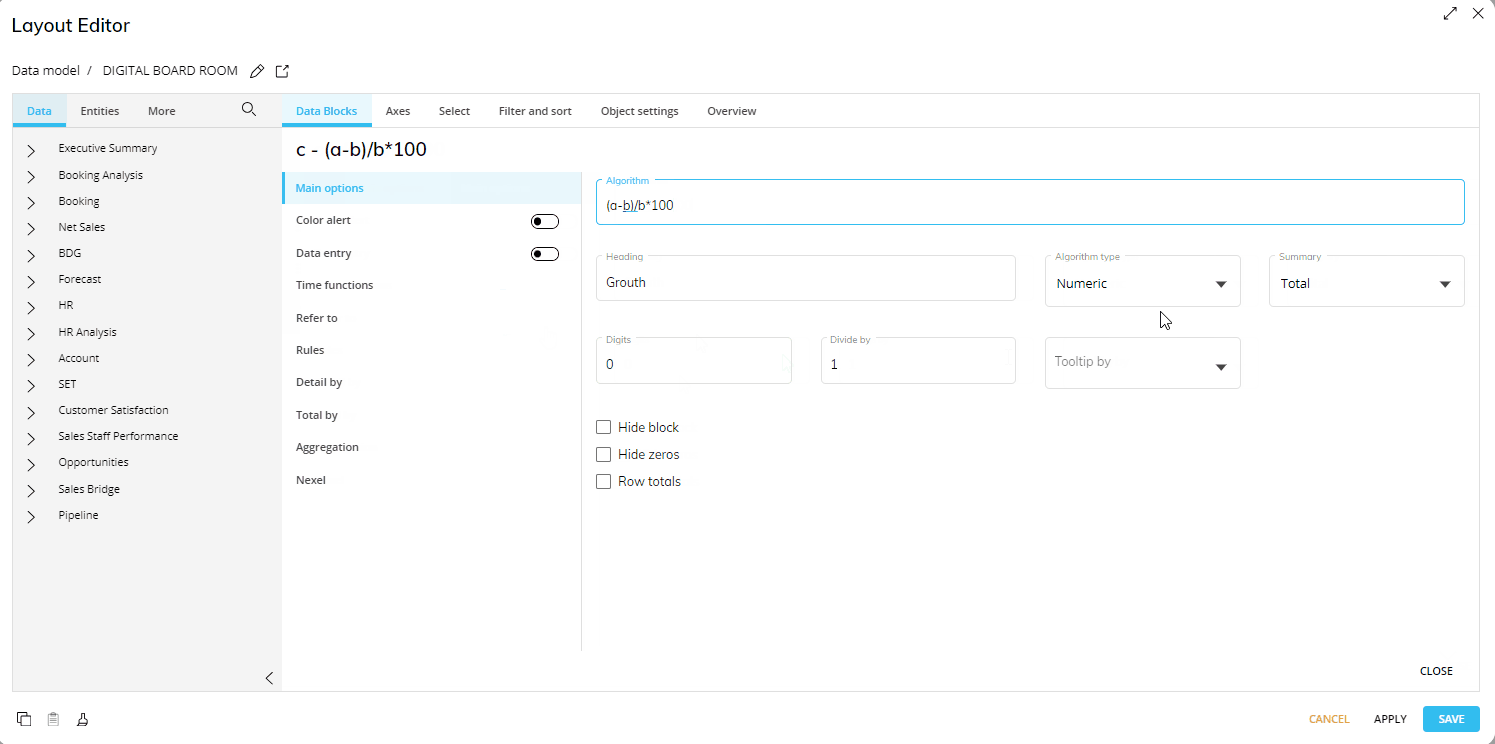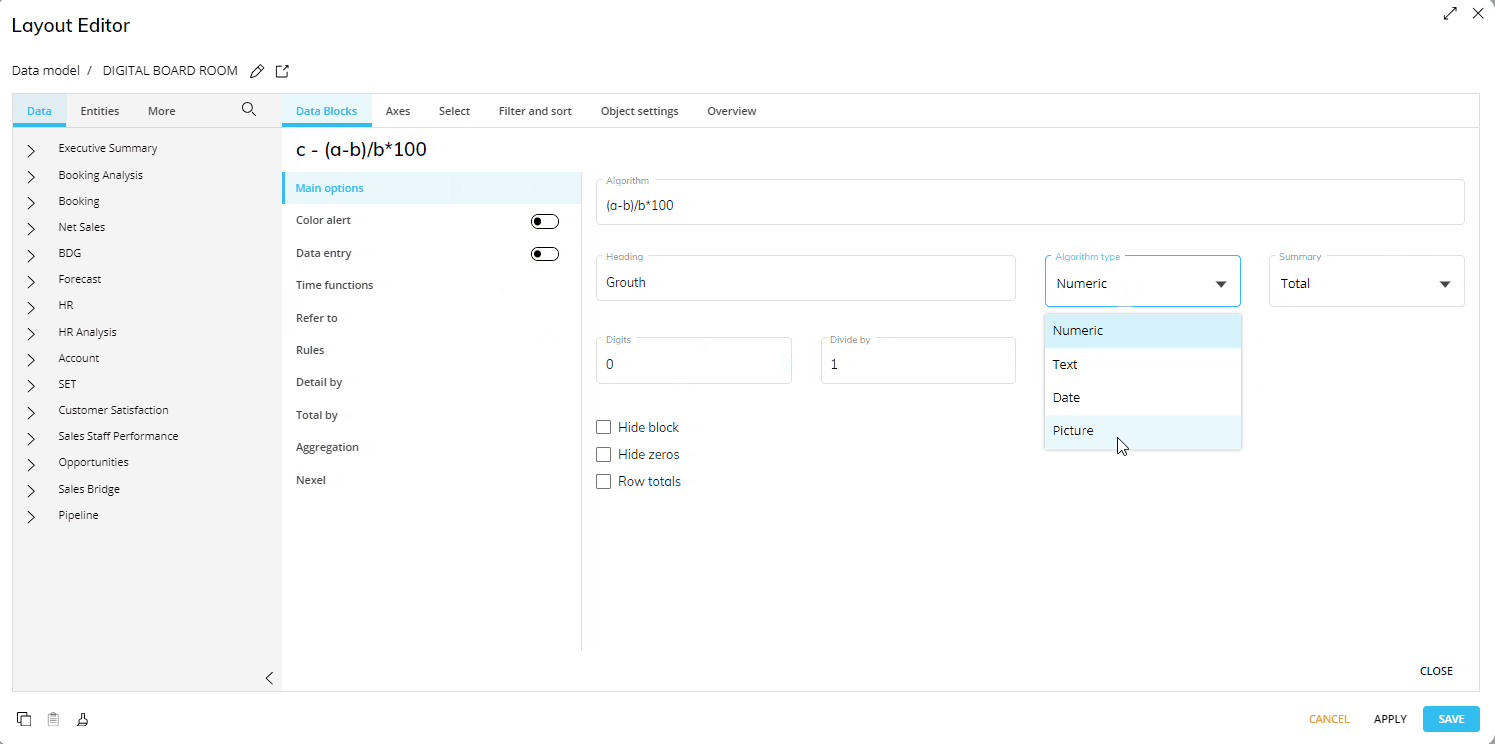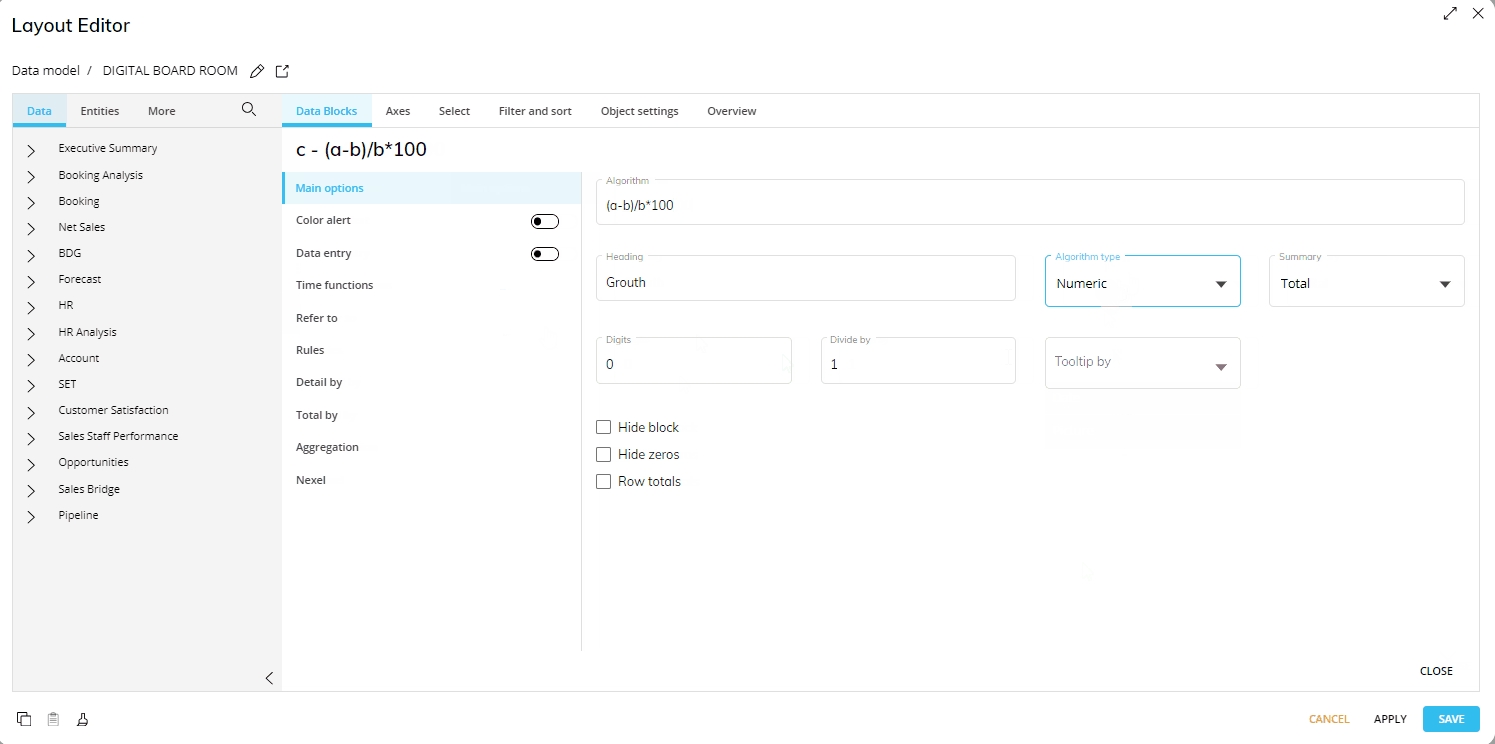
The following example is a report with a Layout having three data blocks:
Block "a" is Gross Sales of the year 2021
Block "b" is Gross Sales of the previous year
Block "c" contains an algorithm that calculates the percentage of variation using the formula (a-b)/b*100.
Formulas use block letters to refer to other Data Blocks and can also refer to other Algorithms. See the table below for a list of the supported operators and functions.
A formula can return the following types of data:
Numeric (default)
Text
Date
Picture
Select the appropriate option from the Algorithm type dropdown list as shown.
The Picture option, (applicable to the Data View, Label, and Button Objects), allows you to display images in the Screen Object. For this to happen, the formula needs to return the name of a picture file and the Picture option must be selected.
The actual image files must first be uploaded to the Capsule. To upload an image, open the Capsule in Design Mode and click on "Images" at the bottom of the left panel under "Resources". Once in the Images section, click on the blue "+ " icon and follow the on-screen instructions. Press "SAVE" to save the image.
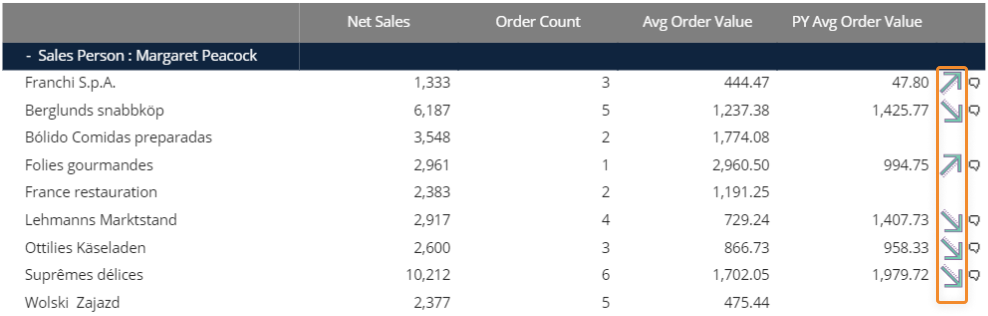
Example of images displayed in a Data View
The highlighted images are the result of a picture algorithm using the following formula:
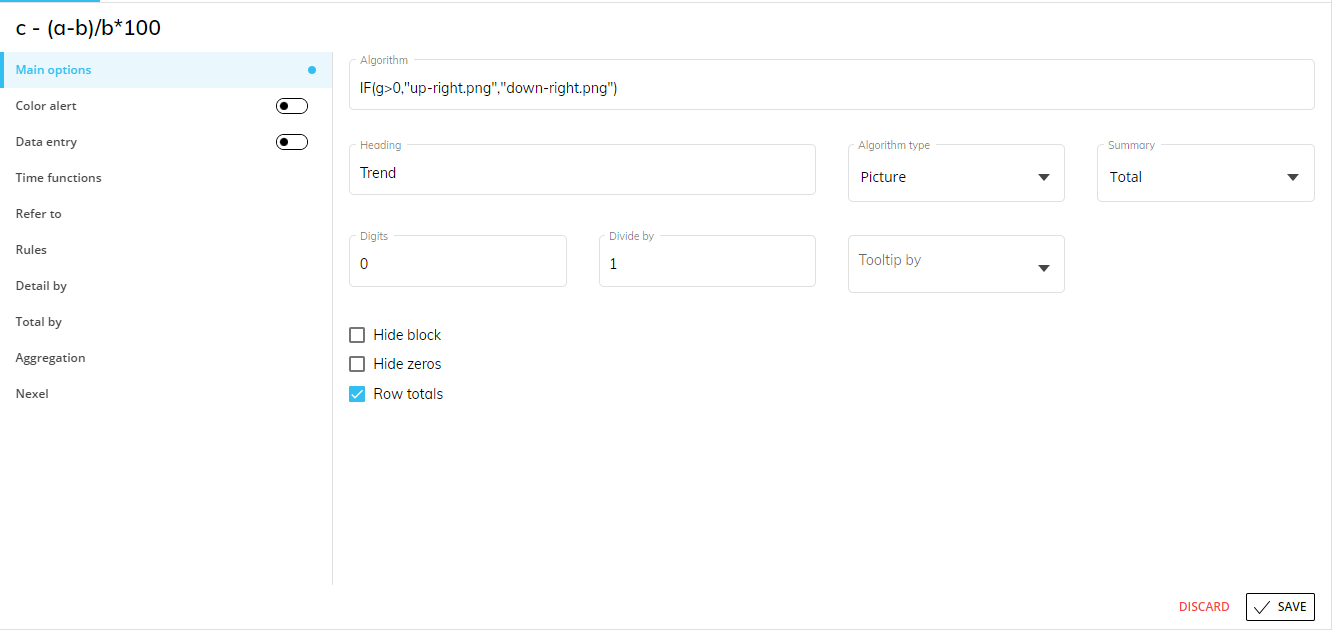
In the formula above, Block "g" refers to a Block that calculates the variance between the average order value and the previous year average order value. If that value is positive (greater than zero), the up-facing arrow is displayed. If that value is negative (less than zero), the down-facing arrow is displayed.
Supported file formats are .jpg, .gif, and .png. The maximum file size is 500 KB.
Supported arithmetic operators
The following table lists all of the supported arithmetic operators that can be used in formulas.
Type | Operator | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Arithmetic | + | Addition | a+b |
- | Subtraction | a-b | |
/ | Division | a/b | |
* | Multiplication | a*b | |
% | Percentage | a/b% is equivalent to a/b*100 a*(1+15%) | |
^ | Exponentiation | a^2 is equal to a*a | |
Comparison | = | Equal to | a=b |
> | Greater than | a>b | |
< | Less than | a<b | |
>= | Greater than or equal to | a>=b | |
<= | Less than or equal to | a<=b | |
<> | Not equal to | a<>b | |
Text | & | Concatenation | a&b concatenates two text strings contained in Block "a" and Block "b" a&"myText" concatenates the string contained in Block "a" with "myText". When using this operator, the result of the algorithm is a text string therefore you must select the option Text from the Algorithm type dropdown list. |
left(text,num_char) | Left substring | Returns the leftmost characters from a text string. Left(a,4) returns the first four characters of the text contained in Block "a". | |
right(text,num_char) | Right substring | Returns the rightmost characters from a text string. Right(a,4) returns the last four characters of the text contained in block "a". | |
mid(text,start_pos,num_char) | Substring | Returns the specified number of characters from a text string starting from the specified position. Mid(a,2,4) returns the four characters starting from position 2 of the text contained in block "a". | |
Supported functions
The following table lists all supported functions that can be used in formulas.
"Function category | Function | Syntax and description | Example | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Board specific | dt | Syntax: dt(column) Returns the column total. To use this function, the Layout must have an entity set by row. | a/dt(a)*100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Board specific | rt | Syntax: rt(column) Returns the row total. To use this function, the Layout must have an entity set by column. | a/rt(a)*100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Board specific | gt | Syntax: gt(column) Returns the grand-total. To use this function, the Layout must have an entity set by row and by column. | a/gt(a)*100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Date and time | DATE | Syntax: DATE(year,month,day) This function returns the DateTime object for a particular date, specified by the year, month, and day. | @DATE returns the current date | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Date and time | DAY | Syntax: DAY(date) This function returns the day number of the month (integer 1 to 31) that corresponds to the specified date. | @DAY returns the current day | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Date and time | MONTH | Syntax: MONTH(date) This function returns the month corresponding to the specified date value. | @MONTH returns the current month | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Date and time | YEAR | Syntax: YEAR(date) This function returns the year as an integer for a specified date. | @YEAR returns the current year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Date and time | TODAY | Syntax: TODAY() Returns the current date | today()-a returns the number of days between the date in Block "a" and the current date, provided a date Cube is in Block "a". today()+a returns a date resulting from the current date plus the number of days specified in Block "a". | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Engineering | CONVERT | Syntax: CONVERT(number,from-unit,to-unit) This function converts a number from one measurement system to its equivalent in another measurement system. | CONVERT(a,day,hr) returns data from Block "a" converted from day format to hour format. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Financial | IRR | Syntax: IRR(arrayvals,estimate) This function returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows represented by the numbers in an array. | IRR(a,x) where "a" is a Block and "x" is a number | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Financial | YIELD | Syntax: YIELD(settle,maturity,rate,price,redeem,frequency,basis) This function calculates the yield on a security that pays periodic interest. | YIELD(a,b,c,d,e,f) where "a" and "b" are dates while "c", "d", "e" and "f" are numbers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Information | ISERROR | Syntax: ISERROR(cellreference); ISERROR(value); ISERROR(expression) This function, Is Error of Any Kind, tests whether a value, an expression, or contents of a referenced cell has an error of any kind. | ISERROR(a/x) where "a" is a Block and "x" is a number | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Information | ISTEXT | Syntax: ISTEXT(cellreference); ISTEXT(value); ISTEXT(expression) This function tests whether a value, an expression, or contents of a referenced cell has text data. | ISTEXT(a) where "a" is a Block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Information | ISNONTEXT | Syntax: ISNONTEXT(cellreference); ISNONTEXT(value); ISNONTEXT(expression) This function tests whether a value, an expression, or contents of a referenced cell has any data type other than text. | ISNONTEXT(a) where "a" is a Block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Information | ISNUMBER | Syntax: ISNUMBER(cellreference); ISNUMBER(value); ISNUMBER(expression) This function tests whether a value, an expression, or contents of a referenced cell has numeric data. | ISNUMBER(a) where "a" is a Block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | AND | Syntax: AND(logical conditions list) Returns True if all conditions are True, otherwise it returns False. | AND(a>0,b<100) returns True if the value in Block "a" is greater than zero and the value in Block "b" is less than 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | OR | Syntax: OR(logical conditions list) Returns True if at least one condition is True. Returns False if all conditions are False. | OR(a>0,b<100) returns True if the value in Block "a" is greater than zero or if the value in Block "b" is less than 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | TRUE | Syntax: TRUE() This function returns the value for logical TRUE. | TRUE(x>y) where "x" and "y" are numbers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | FALSE | Syntax: FALSE() This function returns the value for logical FALSE. | FALSE(x>y) where "x" and "y" are numbers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | NOT | Syntax: NOT(value) This function reverses the logical value of its argument. | NOT(x>y) where "x" and "y" are numbers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | IF | Syntax: IF(valueTest,valueTrue,valueFalse) Returns true_value if the condition is True and false_value if the condition is False. The condition can be any logical expression. | if((a*b)>0,a,c) if(a>100,"Greater", "Lower") if(and(a>0,b>0),a*b,0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Logical | IFERROR | Syntax: IFERROR(value,error) This function evaluates a formula and returns a value you provide if there is an error or the formula result. | IFERROR(a/x,error) where "a" is a Block, "x" is a number and "error" is the value in case of an error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lookup | COLUMN | Syntax: COLUMN(reference) This function returns the column number of a reference. | COLUMN(x)-1 returns the position of the column previous to x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lookup | ROW | Syntax: ROW(reference) This function returns the number of a row from a reference. | ROW(x)-1 returns the position of the row previous to x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lookup | INDEX | Syntax: INDEX(return,row,col,area) This function returns a value or the reference to a value from within an array or range. | INDEX(a,x,y,z) where "a" is a Block and "x", "y" and "z" are numbers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lookup | OFFSET | Syntax: OFFSET(reference,rows,cols,height,width) This function returns a reference to a range. The range is a specified number of rows and columns from a cell or range of cells. The function returns a single cell or a range of cells. | OFFSET(a,x,y) where "a" is the location from which to base the offset while "x" and "y" are numbers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lookup | MATCH | Syntax: MATCH(value1,array,type) This function returns the relative position of a specified item in a range. | MATCH(x,a) where "x" is the value to search for and "a" is a Block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Math and trigonometry | ABS | Syntax: ABS(number) Returns the absolute value of a number. | ABS(a-b) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Math and trigonometry | ROUND | Syntax: ROUND(value,places) This function rounds the specified value to the nearest number, using the specified number of decimal places. | ROUND(a*b,2) return the result of the multiplication between "a" and "b" with 2 decimal places | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Math and trigonometry | SUBTOTAL | Syntax: SUBTOTAL(functioncode,value1,value2,...); SUBTOTAL(functioncode,array) This function calculates a subtotal of a list of numbers using a specified built-in function. | SUBTOTAL(functioncode,x,y) where "x" and "y" are numbers and "functioncode" is a number as follows:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Math and trigonometry | SUM | Syntax: SUM(value1,value2,...); SUM(array); SUM(array1,array2,...) This function returns the sum of cells or range of cells. | SUM(a) returns the sum of the values in "a" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Math and trigonometry | SUMIF | Syntax: SUMIF(array,condition,sumrange) This function adds the cells using a given criteria. | SUMIF(a,a>0,b) where "a" and "b" are Blocks | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statistical | AVERAGE | Syntax: AVERAGE(value1,value2,...); AVERAGE(array); AVERAGE(array1,array2,...) This function calculates the average of the specified numeric values. | AVERAGE(a,b) where "a" and "b" are Blocks | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statistical | COUNT | Syntax: COUNT(value1,value2,...); COUNT(array) This function returns the number of cells that contain numbers. | COUNT(a) where "a" is a Block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statistical | MAX | Syntax: MAX(value1,value2,...); MAX(array); MAX(array1,array2,...) This function returns the maximum value, the greatest value, of all the values in the arguments. | MAX(a) returns the highest value in "a" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statistical | MIN | Syntax: MIN(value1,value2,...); MIN(array); MIN(array1,array2,...) This function returns the minimum value, the least value, of all the values in the arguments. | MIN(a) returns the lowest value in "a" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | CHAR | Syntax: CHAR(value) This function returns the character specified by a number. | CHAR(x) where "x" is a number | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | CONCATENATE | Syntax: CONCATENATE(text1,text2,...) This function combines multiple text strings or numbers into one text string. | CONCATENATE(x,y) where "x" and "y" are numbers or text | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | LEN | Syntax: LEN(value) This function returns the length of a text string (the number of characters). | LEN(a) returns the length of "a" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | MID | Syntax: MID(text,start_num,num_chars) This function returns the requested number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify. | MID(x,3,4) returns four characters that follow the third letter in the text "x" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | RIGHT | Syntax: RIGHT(text,num_chars) This function returns the specified rightmost characters from a text value. | RIGHT(x,3) returns the last 3 characters on text "x" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | LEFT | Syntax: LEFT(text,num_chars) This function returns the specified leftmost characters from a text value. | LEFT(x,3) returns the first 3 characters on text "x" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | SUBSTITUTE | Syntax: SUBSTITUTE(text,old_piece,new_piece,instance) This function substitutes a new string for specified characters in an existing string. | SUBSTITUTE(x,y,z,3) returns the text "x" including "z" in place of the third "y" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | TRIM | Syntax: TRIM(text) This function removes extra spaces from a string and leaves single spaces between words. | TRIM(x) where "x" is text | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text | VALUE | Syntax: VALUE(text) This function converts a text string that is a number to its numeric value. | VALUE(two) returns "2" |
Formulas in Algorithms must always be written using English syntax and function names, as shown in the tables above. Localized versions of function names are not supported (e.g. IF is valid, while the Italian SE is not).
The examples in the table above use the comma as the list separator character. However, both the comma (,) and the semicolon (;) are supported as list separators in formulas. This behavior is consistent across all environments and does not depend on the regional settings of the user’s computer.
It is the user's responsibility to understand how to apply the formulas appropriately in each context.