This topic describes how to customize Cube visibility for individual users by creating Cube visibility rules.
The Cube visibility feature makes it easy to define an extremely granular data access level right into the Data Model itself, for each user and for each cell of Cubes, providing a significant amount of control and flexibility in determining who can access and perform data entry actions on specific Cubes.
It also acts as a security layer that enhances Board's standard security by allowing administrators to create free data access models based on custom access and locking conditions that rely on dedicated grant Cubes for applying access level rules to physical cells of data Cubes.
The Cube visibility feature has a great impact on the read/write workflow in Board, as it greatly speeds up the configuration and management of data access, and, at the same time, offers the possibility to create very specific rules for each Data Model security profile.
When defining the security in the Data Model Security Profile section, keep in mind that:
The manual security selections are overwritten by the "Custom Selection Script" if the Selects are applied to the same Entities.
The Custom selection script can be populated manually and make use of variables like @User or any custom User Metadata defined in the Subscription Hub.
The result of these two selections is then further restricted by the "Select based on Cube" security.
Finally, the "Cube visibility" is applied.
Security features of Cube visibility at a glance:
Always active regardless of any changes that the user can make to Layouts and any selections applied in Play Mode.
Prevents users from writing into Cube cells where they should not be permitted to do so.
Cube visibility rules are calculated and applied in real time for each aggregated cell during the data retrieval phase: any change in the authorizations is immediately reflected in Screens and other Board resources (after a page refresh). Since the Access and Locking conditions are based on grant Cubes, you can dynamically change permissions by performing data entry actions on Data Views having said Cubes in the Layout with, of course, Data Entry enabled.
Each Cube visibility rule is automatically applied to:
Layouts.
Selections (only when a Dynamic Select or a "Select based on Cube" is made on a Cube with a visibility rule).
All Procedures steps involving Layouts (except Dataflows) check.
Smart Import Objects. Currently, Smart Import Objects respect only Access and Locking conditions set on Cube visibility rules. Default access permissions (Read/Write, Read only, and No access) are ignored, just like with the Data Reader Check before release.
Cube visibility rules are currently ignored by:
Dataflows and Data Readers. Both Procedure steps always consider and write to the entire dataset stored in Cubes, and are only affected by selections.
Data Pickers. Data Pickers can always be configured in order to retrieve values from any cell of the Cube.
Reverse Rules. Reverse Rules are always allowed to write to any cell of the Cube, as per their configuration.
Nexel layers. Nexel formulas always consider and write to the entire dataset stored in Cubes and are only affected by selections.
Data entry-enabled Data Blocks with the "Pattern-based allocation" option turned on. Data allocation based on a Cube always considers its entire dataset to obtain a correct pattern.
RDB (Rolap) Cubes.
If a Cube is affected by a Cube visibility rule, you cannot enable the "Cube cell locked by" option on it in the Layout editor: if you do, the Layout execution will fail.
Cube visibility table
Cube visibility rules can be defined from the Data Model Security section of each Data Model. When editing or creating a new security profile, a new table in the "Data Model Profile options" sliding panel allows you to manage/review Cube visibility rules.
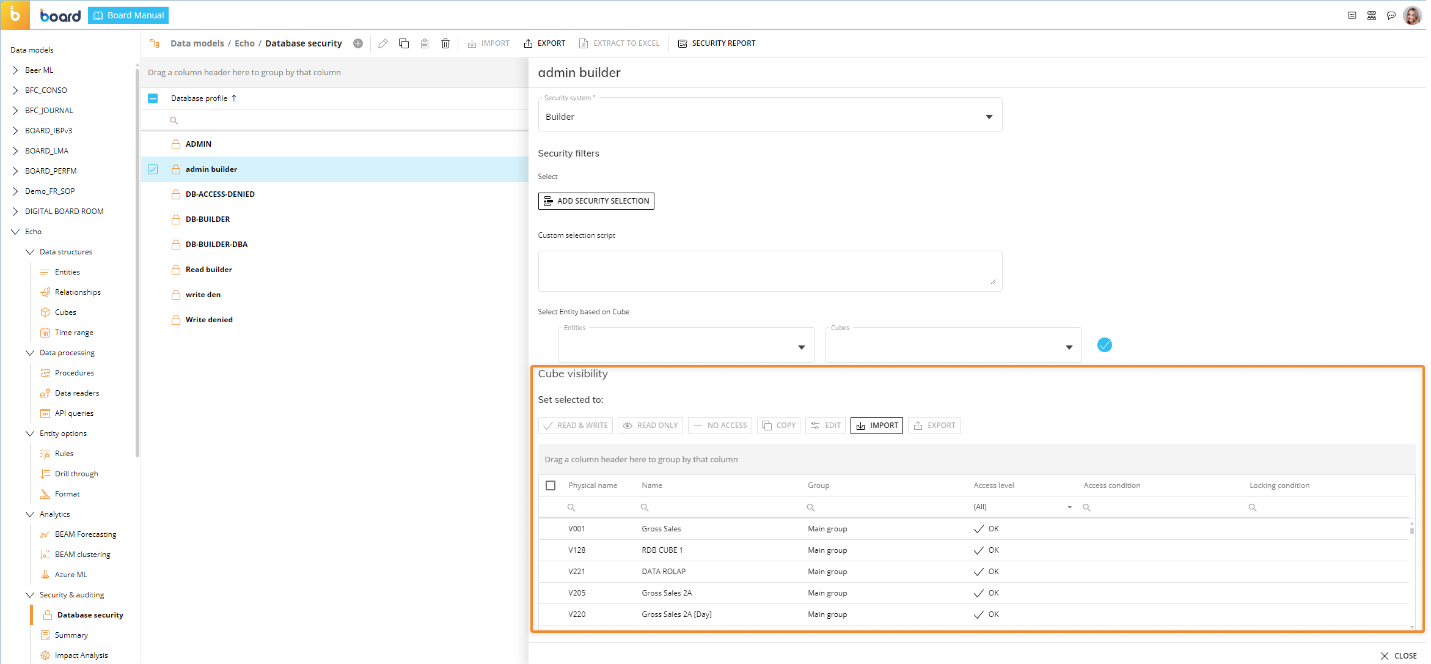
The Cube visibility table is sortable and searchable using the interactive header fields on each column. It also allows for single and multiple selection of rows, using the checkboxes in the first column.
The default access level for Cubes is Read/Write. You can copy and paste an existing Cube visibility rule right from the table by selecting the desired row and using the Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V keyboard shortcuts or by using the "COPY" and "PASTE" buttons that appear above the table. The "COPY" button is active only when a single row is selected, while the "PASTE" button is active for both single and multiple row selections. When you hover over a condition that doesn’t fit in the corresponding cell, a tooltip appears showing the condition in full. The conditions shown in the "Access condition" and "Locking condition" cannot be edited directly in the table: you can only copy the settings of the entire row (access level and conditions) and paste them on other rows.
From the table, you can apply default access level permissions (Read/Write, Read only, and No access) by selecting one or more rows and by clicking on the corresponding button above the table. The "EDIT" button opens the Advanced access settings configuration window. This configuration window also opens when the user double-clicks on an Access condition cell or Locking condition cell in the table. See next paragraph for more details.
Creating Cube visibility rules
To create a new rule:
Select a Cube in the Cube visibility table.
Define the desired access level by clicking on the corresponding button above the table. The available default access levels are the following:
Read/Write. This level grants permission to enter data into the Cube and run update Procedures. Access to the Data Model design features is not affected by this configuration, as it is based on the user's license.
Read only. This level grants read-only access to the data stored in the Cube. Users with this profile can view values in reports coming from the Cube or run update Procedures, but they cannot enter data.
No access. This level completely denies any access to the Cube. Users will not be able to view values coming from it in reports or run update Procedures.
You can further refine access permissions with advanced Access and Locking conditions by clicking on the "Edit" button above the table. This will open the advanced access settings configuration window.
Set access and/or lock conditions in the "Grant cells access where" or "Deny cell editing where" sections.
To create a new condition, proceed as follows:
Select a grant Cube from the dropdown menu. The dropdown supports auto-suggest: the input field reveals options for the user to select from as a text string is typed.
Grant Cubes are numeric Cubes whose values regulate which cells of the Cube selected in step 1 can be edited and/or viewed by the user.
Define the comparison condition from the next dropdown menu. The only comparison conditions available are "< > 0" (not 0) or "= 0" (equal to 0).
Define a logical operator to logically join the condition with the following ones. The only logical operators available are "And" and "Or". Logical operators combine relations according to the following rules:
And. Both conditions must be true for the entire condition to be true.
Or. If either condition is true, then the entire condition is true.
The logical operator set in the first row is always applied to the following rows (it is not possible to configure mixed AND and OR conditions).
Save the condition using the blue tick icon ( ✔ ) at the end of each row.
You can add as many conditions as needed by starting over from step 1. You can delete previously saved conditions by clicking on the red recycle bin icon at the end of each row.
Click on "APPLY" to save and close the advanced access settings configuration window.
The "Grant cells access where" or "Deny cell editing where" menus are enabled or disabled depending on the Access level configured in the "Data Model Profile options" sliding panel. When one or both menus are disabled, they are grayed out as per the table below.
Grant cells access where | Deny cell editing where | |
|---|---|---|
Read/Write | Enabled | Enabled |
Read only | Enabled | Disabled |
No access | Disabled | Disabled |
If one of the menus includes previously saved conditions and is disabled, the conditions are saved but they no longer affect data access control. If the menu is enabled again, the conditions will also become effective again.
If the Advanced access settings configuration window is opened after selecting multiple Cubes in the table, and those Cubes have different access settings, the fields that aren’t matching will show a "Mixed" label. In this case, changing and saving the settings will affect all selected Cubes and overwrite any existing individually configured conditions.
Example
Let's consider the following configuration for the "User" security profile.
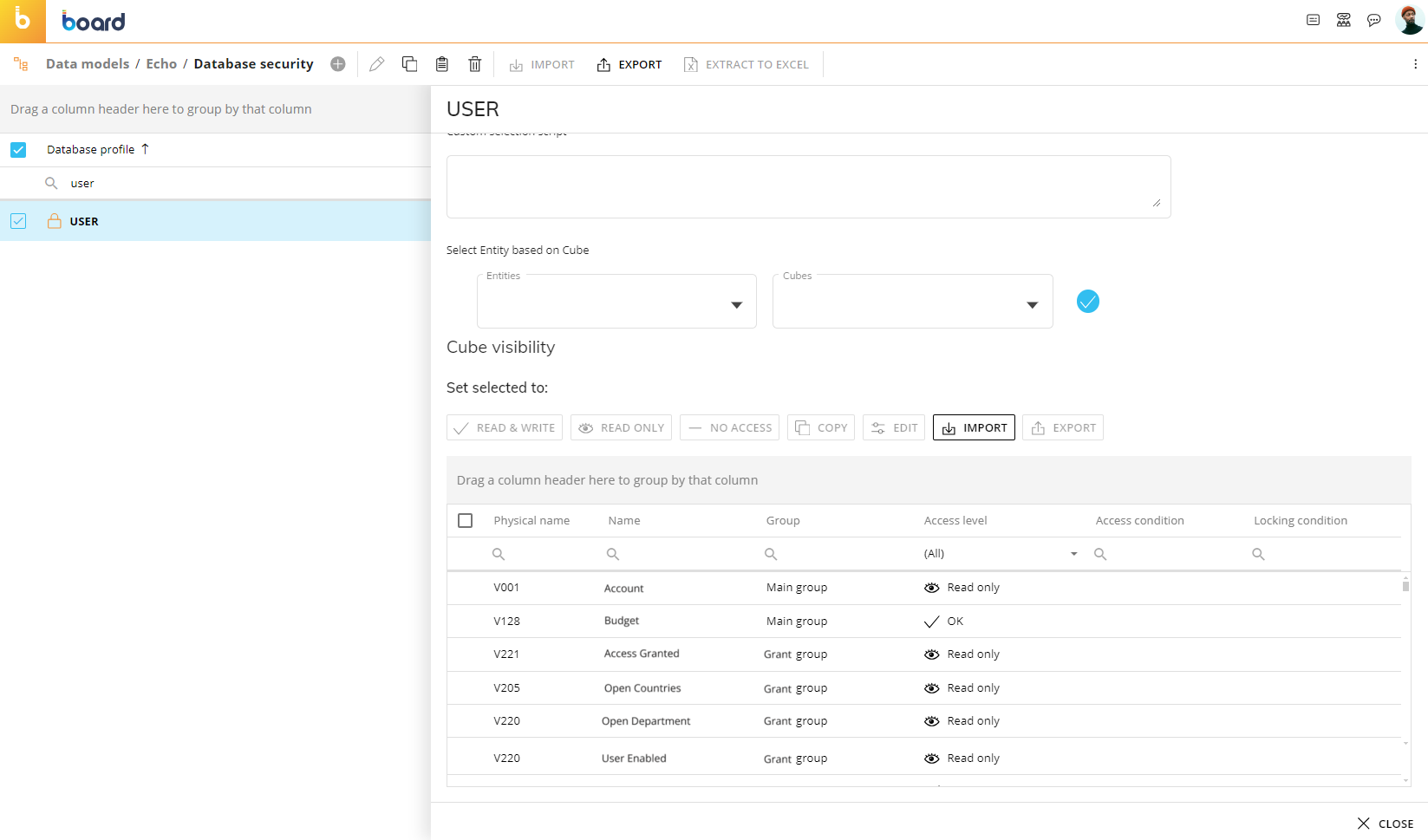
As you can see, the "Actual" and "Budget" Cubes have been configured via specific Access and Locking conditions. These conditions are based on four grant Cubes that regulate which user is able to read and/or write on the Actual and Budget Cubes and on which combinations of the Entities in their structure.
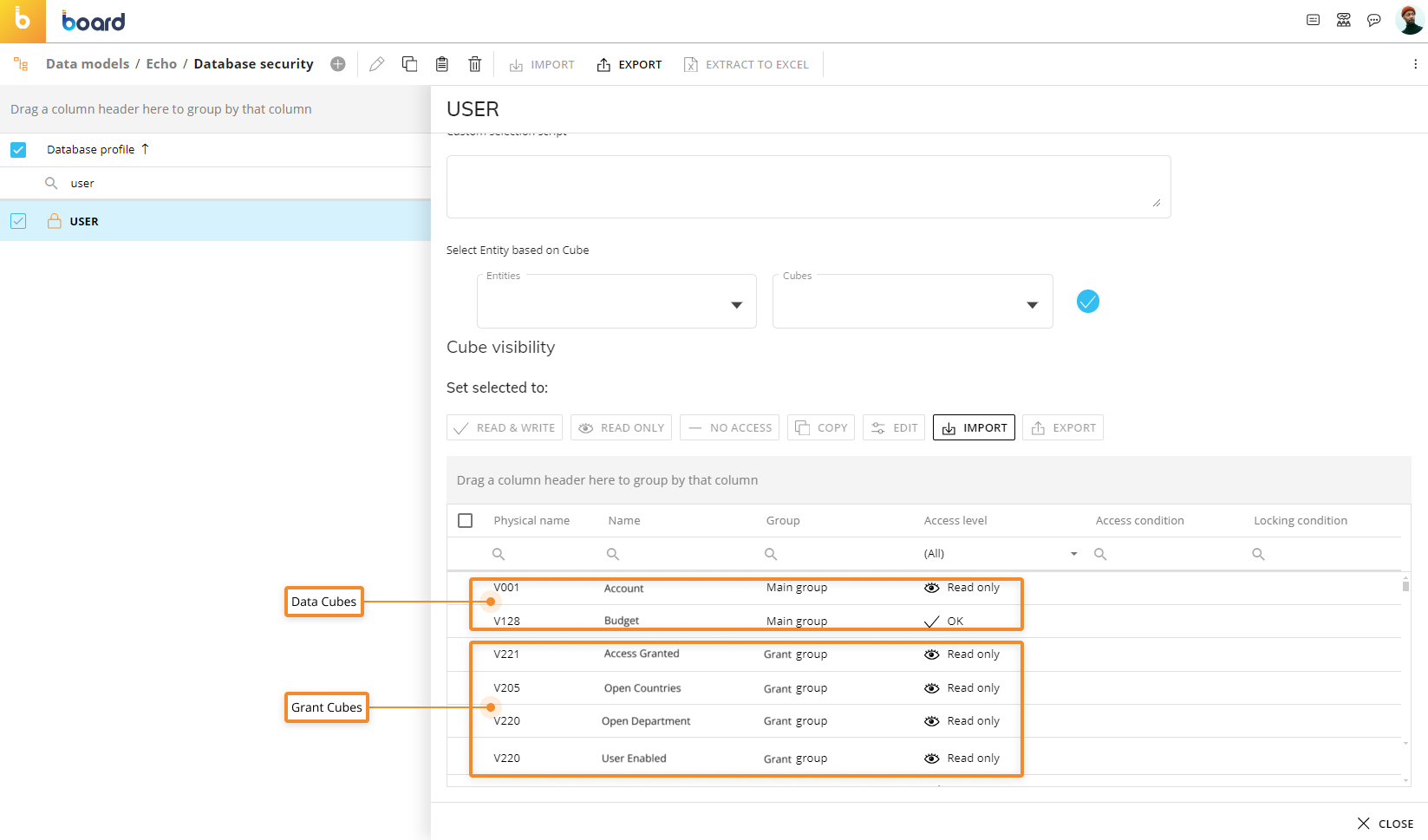
By creating a simple administrative Screen with four Data Views that each have a single grant Cube in their Layout with Data Entry enabled, you can dynamically change permissions for each user.
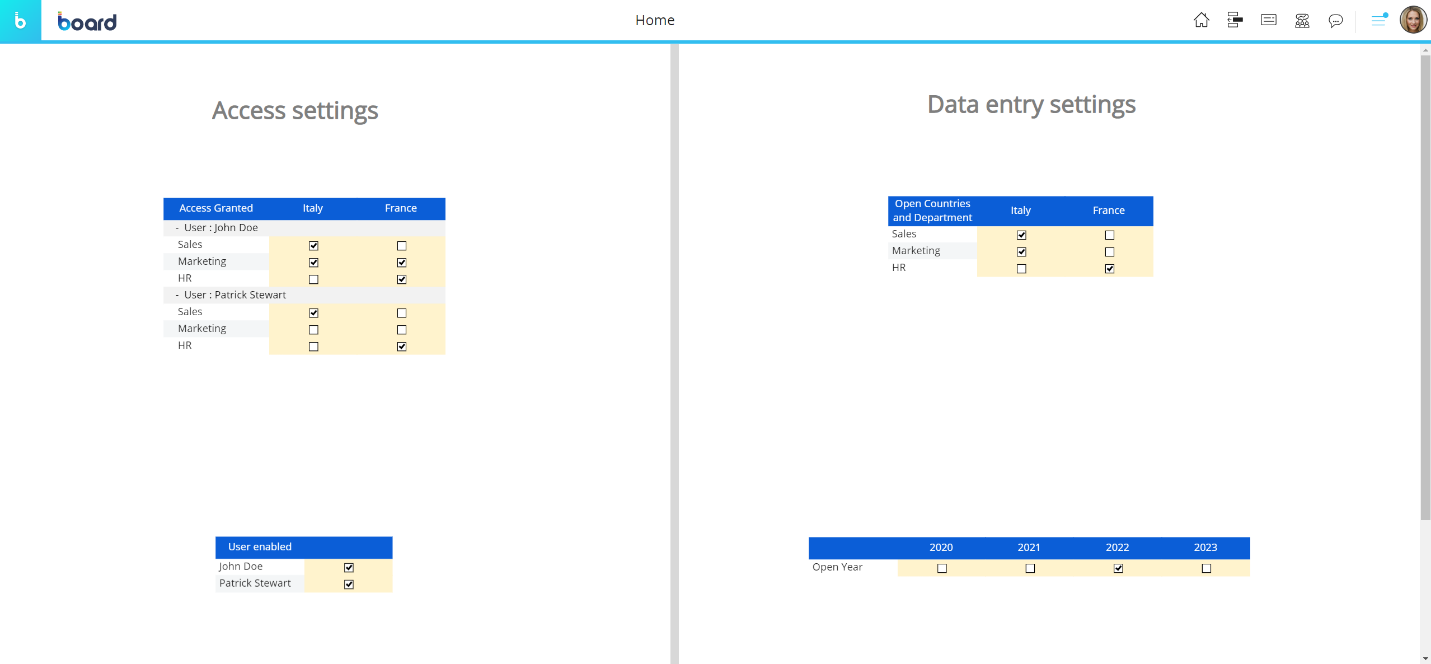
With the configuration shown above, the user John Doe can access specific combinations of the "Actual" and "Budget" Cubes (Sales and Marketing for Italy and HR for France). The following image shows the data that can be accessed by the user.
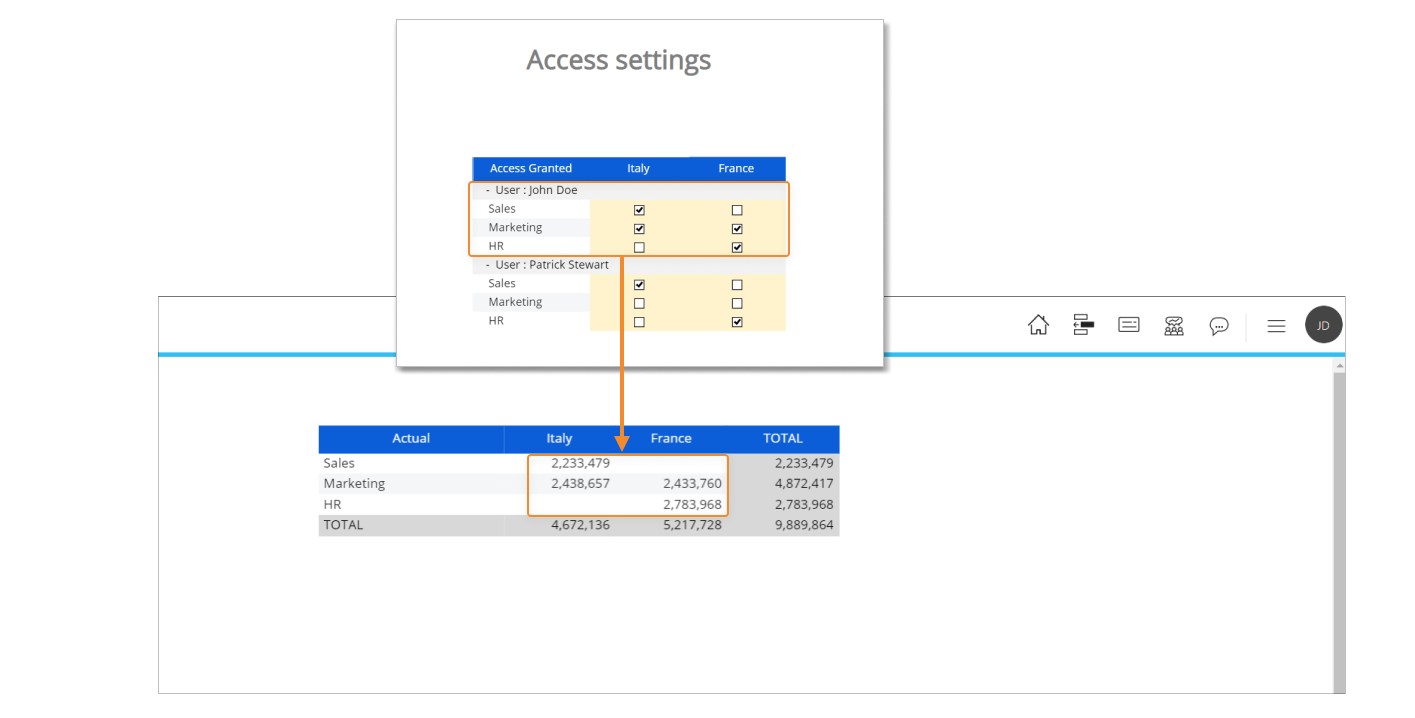
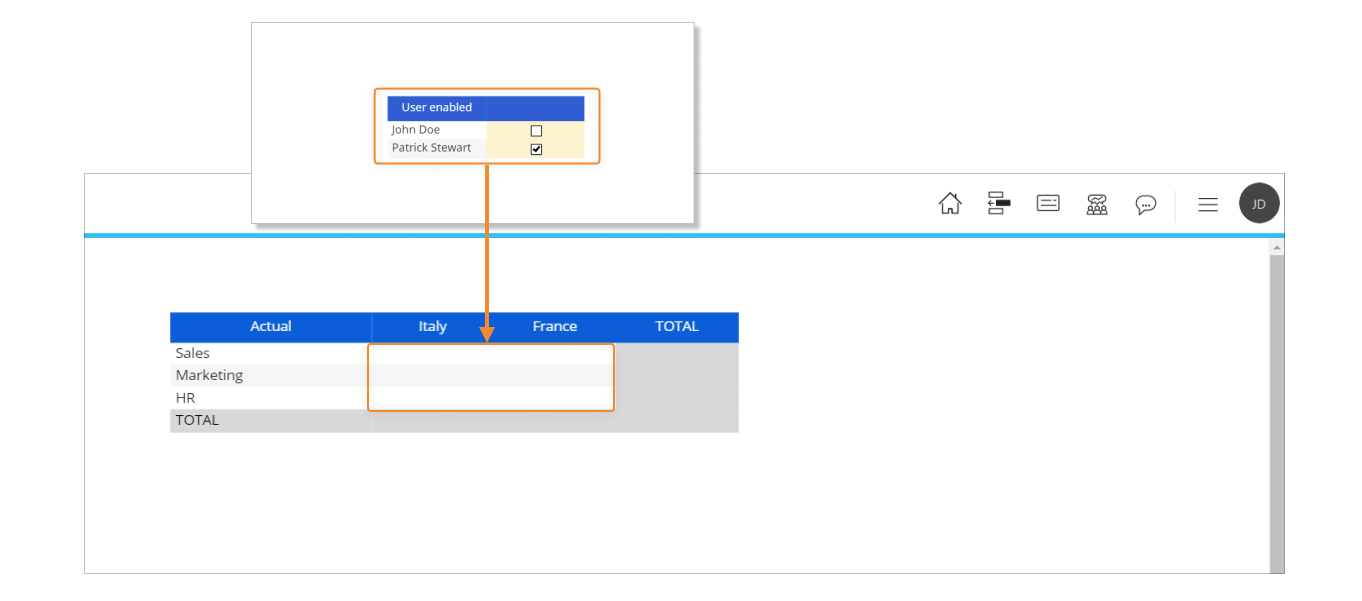
If we disable the user John Doe, he will not have access to any data stored in the Cube. If we refresh the Screen, no data will be shown anymore.
Now let's focus on the "Data entry settings" section of the administrative Screen. The upper Data Views in that section determines which combinations of Department and Country (the Entities in the structure of the Budget Cube) the user John Doe can perform data entry actions on.
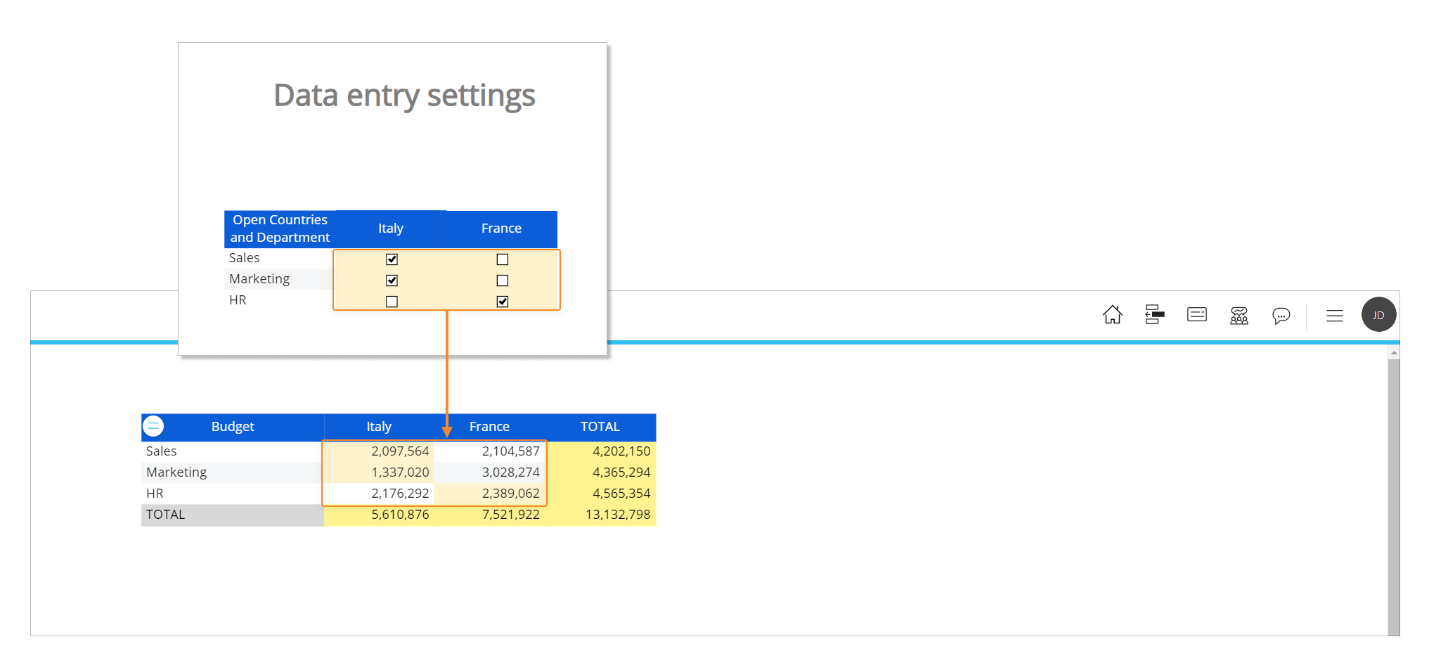
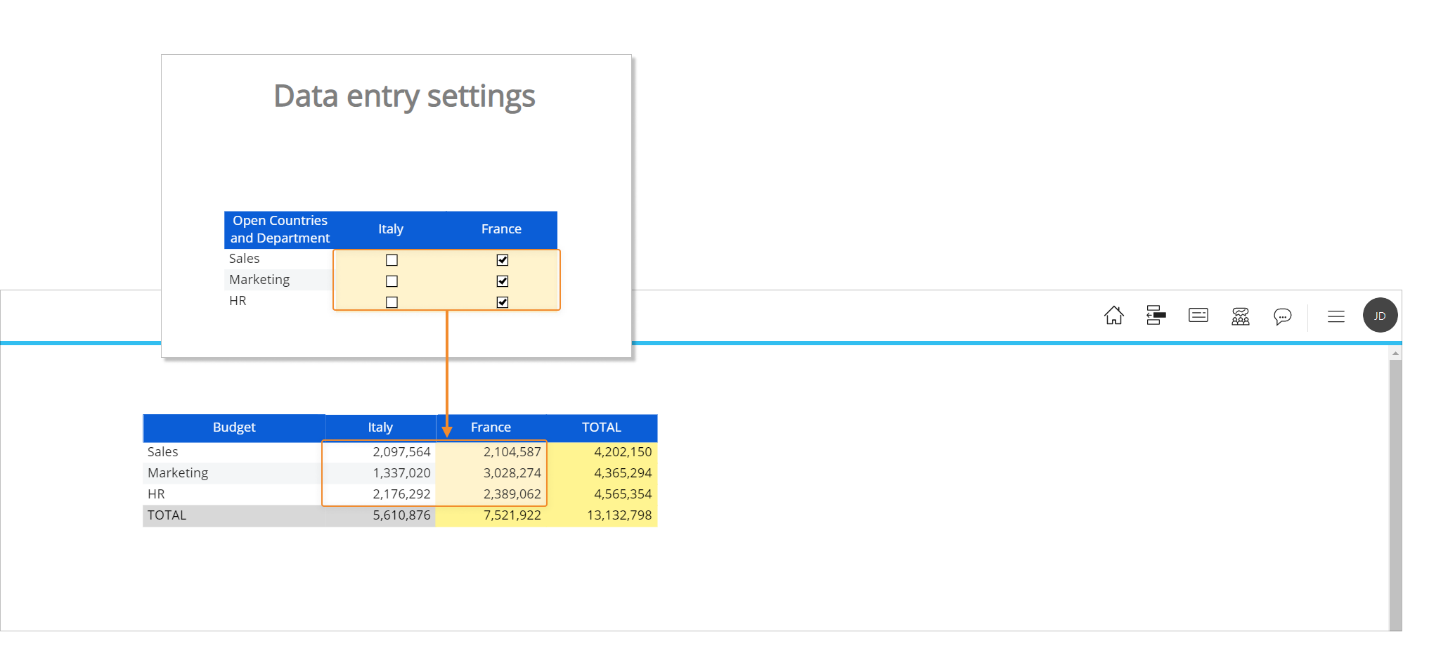
If we change permissions for the user, data entry-enabled cells will change accordingly as we can see in the following image.
Cube visibility settings export/import
The export/import feature has been extended to the Cube visibility configurations to give you a much more flexible and efficient way of configuring Data Model Security Profiles, especially when you need to copy and paste all or some Cube visibility configurations from one security profile to another.
To export the Cube visibility configurations of a Data Model Security Profile, select the desired Cube visibility configurations under the Cube visibility section and click "EXPORT". A file containing the selected Cube visibility configurations will be downloaded to your local machine and will have the following name: cube_visibility_export.bcv.
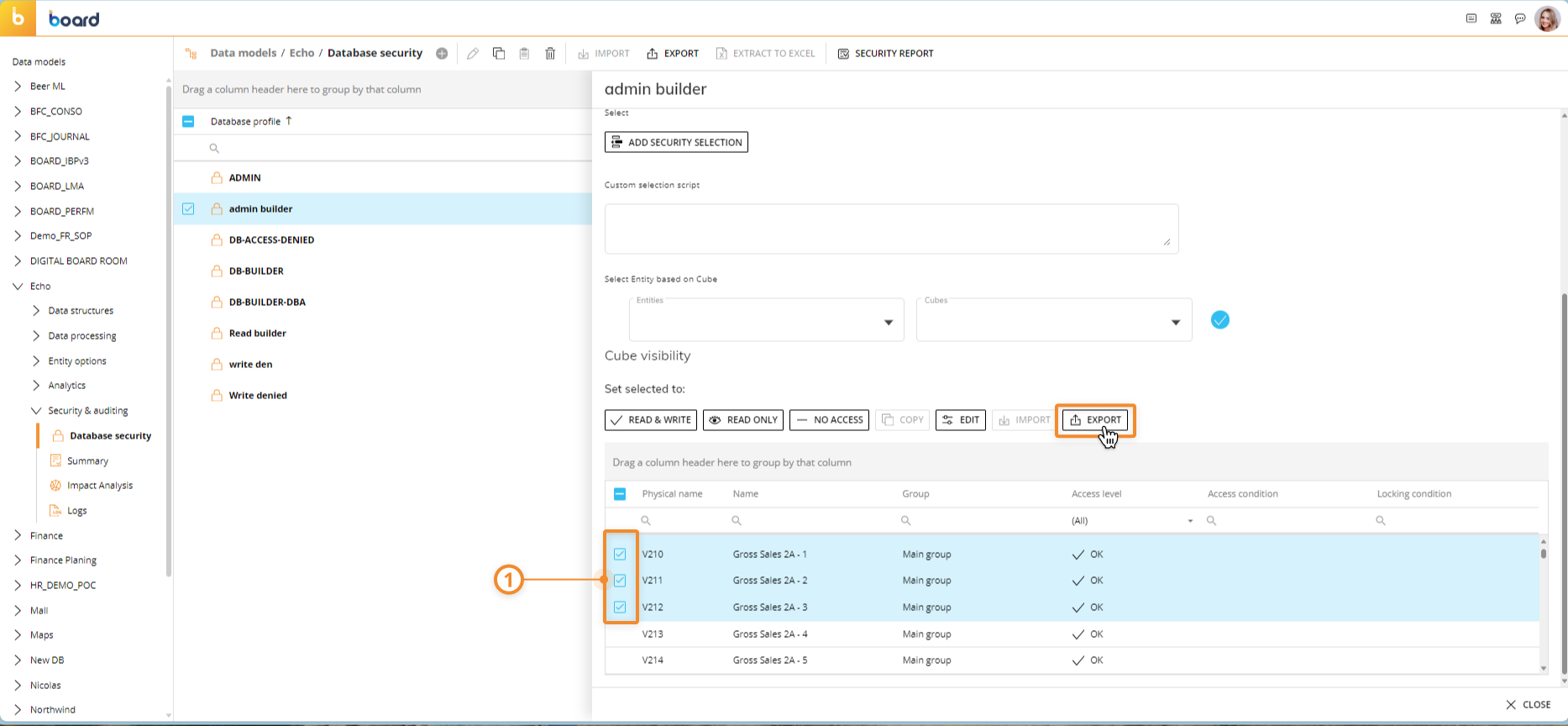
To import the Cube visibility configurations from a .bcv file into a Data Model Security Profile:
Open the "CUBE VISIBILITY" menu of the desired Data Model Security Profile and click "IMPORT" to open the upload popup window.
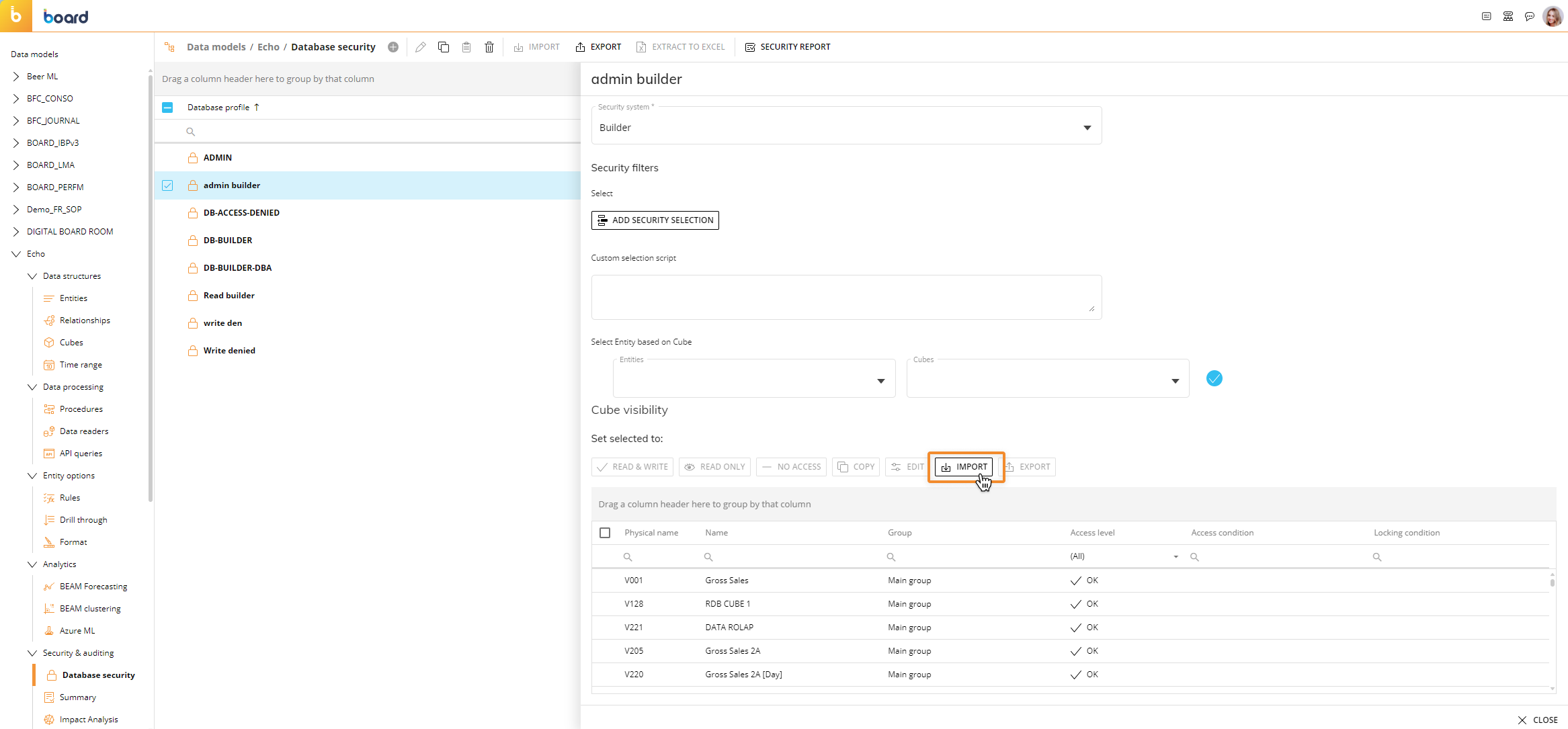
Click "BROWSE FILE" or drag and drop the .bcv file that contains the desired Cube visibility configurations, then click the "IMPORT" button.

Click "CREATE".
The maximum file size limit is 1MB.
The import action will overwrite all Cube visibility rules based on the Physical name of the Cube with which they are associated.
The import action does not import Cubes. It only imports the Cube visibility configurations of Cubes that already exist in the target Data Model and which have the same given name and Physical name as those in the .bcv file.